Physiotherapy vs physical therapy, are they the same? This article examines the differences and helps you choose the best option for your needs. Key Takeaways Physiotherapy and physical therapy, while often used interchangeably, differ in terminology and focus; physiotherapy adopts a holistic approach, while physical therapy emphasizes exercise-based rehabilitation.Physiotherapists utilize hands-on techniques such as manual …
Physiotherapy vs Physical Therapy: Key Differences Explained
Physiotherapy vs physical therapy, are they the same? This article examines the differences and helps you choose the best option for your needs.
Key Takeaways
-
Physiotherapy and physical therapy, while often used interchangeably, differ in terminology and focus; physiotherapy adopts a holistic approach, while physical therapy emphasizes exercise-based rehabilitation.
-
Physiotherapists utilize hands-on techniques such as manual therapy and muscle energy techniques, whereas physical therapists primarily focus on prescribed exercise plans and modalities to alleviate pain and improve function.
-
Training and qualifications for physiotherapists and physical therapists vary by region, with distinct educational pathways and licensure requirements reflecting local standards in practice.
Defining Physiotherapy and Physical Therapy
The terms “physiotherapy” and “physical therapy” are often used interchangeably in different parts of the world. In the U.S., “physical therapist” is the preferred term, while “physiotherapist” is more commonly used elsewhere. Despite the varying terminology, these professions share the same core goals and practices.
Historically, there has been no formal distinction in the care goals or scope of these professions. Both physiotherapy and physical therapy aim to address pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall physical function. These three overarching goals are at the heart of both practices, reflecting their shared commitment to patient well-being.
What truly matters is the quality of service delivered by qualified healthcare professionals. Whether you see a physiotherapist or a physical therapist, the focus is on promoting recovery and maintaining physical function through various physical methods and hands-on therapies.
Core Focus Areas of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy takes a holistic approach to treatment, addressing not just the physical aspects of recovery but also the psychological factors that can impact healing. This comprehensive method aims to improve not only physical health but overall well-being.
A key focus in physiotherapy focuses on promoting physical activity, which helps in fostering long-term wellness and preventing injuries. Physiotherapists promote movement and exercise to help patients maintain physical fitness and enhance their quality of life.
Additionally, physiotherapists often employ hands-on treatment approaches, providing more direct physical manipulation and manual therapy compared to physical therapists. This hands-on approach is crucial in treating musculoskeletal problems and restoring physical function.
Core Focus Areas of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy, on the other hand, primarily focuses on medical care aimed at easing pain and improving movement through exercise-based interventions. The primary technique used in physical therapy is physical exercise, which differentiates it from the more hands-on approach of physiotherapy.
Physical therapy aims to relieve pain, improve movement, and prevent or recover from injuries. Therapists create prescribed physical therapy exercise plans tailored to each patient’s needs, helping them resume daily activities through a physical therapy program. Additionally, physical therapy focuses on enhancing overall well-being.
Patients are encouraged to perform prescribed exercises at home, promoting independence and active participation in their recovery.
Techniques Used in Physiotherapy
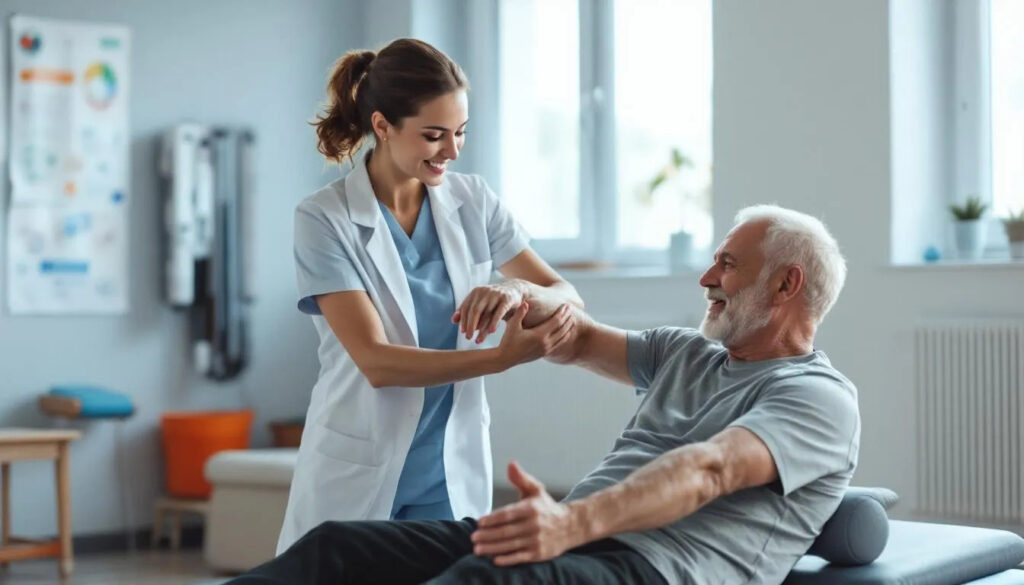

Manual therapy is a cornerstone of physiotherapy, involving hands-on techniques and manual techniques to alleviate pain and enhance movement. Techniques like joint mobilization and joint manipulation improve motion, joint function, and pain control through the manual therapy technique.
Minimal energy techniques (MET) uses the muscle’s own energy to relax and lengthen muscles, enhancing overall movement. Instrument-assisted soft tissue techniques mobilization (IASTM) employs specialized tools to manipulate soft tissues, promoting injury repair and reducing scar tissue through autogenic or reciprocal inhibition.
Friction massage enhances blood flow and releases tight areas around joints, facilitating recovery and reducing pain. Dry needling targets trigger points in muscles to relieve myofascial pain, causing localized tissue response that aids in pain relief.
Additional techniques include:
-
Trigger point therapy, which focuses on relieving muscle tightness by applying pressure to specific muscle knots.
-
Kinesiotaping, which provides support and stability to muscles and joints without restricting movement.
-
Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA), which identifies dysfunctional movement patterns that may lead to pain and injury.
Techniques Used in Physical Therapy
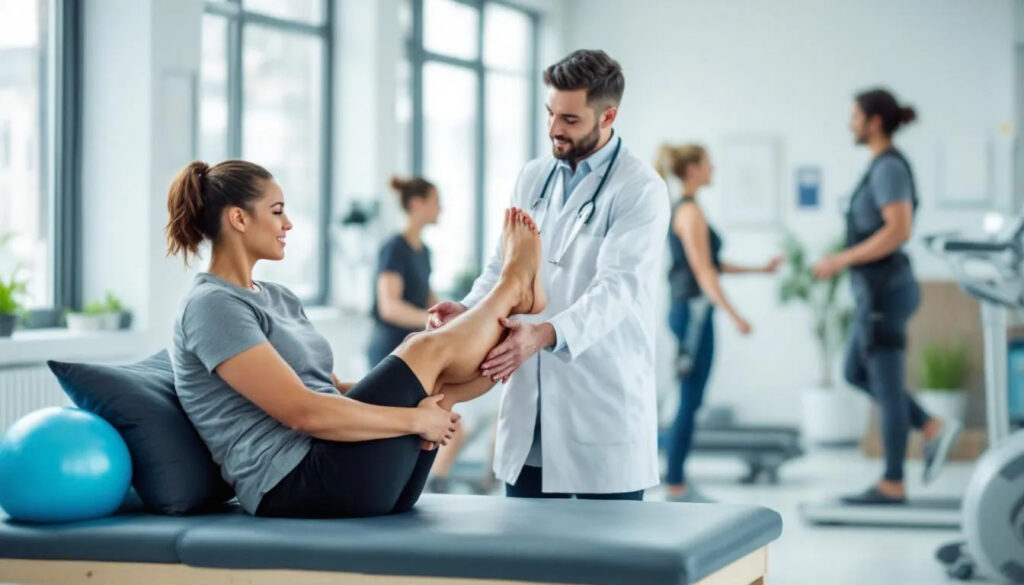

Physical therapists commonly use the following methods to aid in patient recovery:
-
Exercise routines
-
Exercise based therapy
-
Hot and cold therapies
-
Physical therapy treatments
-
Ultrasound
-
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
These methods help in managing pain and improving physical function. They are particularly effective in treating musculoskeletal problems and ease pain associated with chronic pain and acute pain.
Advanced methods such as other techniques:
-
Cryotherapy
-
Thermotherapy
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
-
Magnetic field therapy are increasingly being utilized to enhance treatment effectiveness and promote faster recovery.
Training and Qualifications
Training and qualifications for physiotherapists and physical therapists vary by region. In the U.K., aspiring physiotherapists must complete a Bachelor of Science degree lasting approximately three years. Globally, the training duration often extends to four years.
In contrast, to become a physical therapist in the U.S., one needs a Bachelor’s degree followed by a Doctoral program in physical therapy. Physical therapists in the U.S. must hold a Doctor of Physical Therapy degree and pass a state licensure exam to practice.
The governing bodies for physical therapy include the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) in the U.S. and the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy (CSP) in the U.K. After acquiring 2,000 hours of clinical experience, U.S. physical therapists can pursue board certification from the American Board of Physical Therapy Specialties.
Work Environments and Settings
Physiotherapists work in various settings, including:
-
Hospitals
-
Outpatient clinics
-
Rehabilitation centers
-
Nursing homes
These environments allow them to address a wide range of patient needs, from acute injuries to treat acute chronic conditions.
Physical therapists often work in diverse environments such as:
-
Private practices
-
Rehabilitation centers
-
Gyms
-
Sports facilities
This diversity enables them to cater to patients with different needs, promoting an active life and helping them manage or recover from chronic conditions.
Treatment Goals and Patient Outcomes
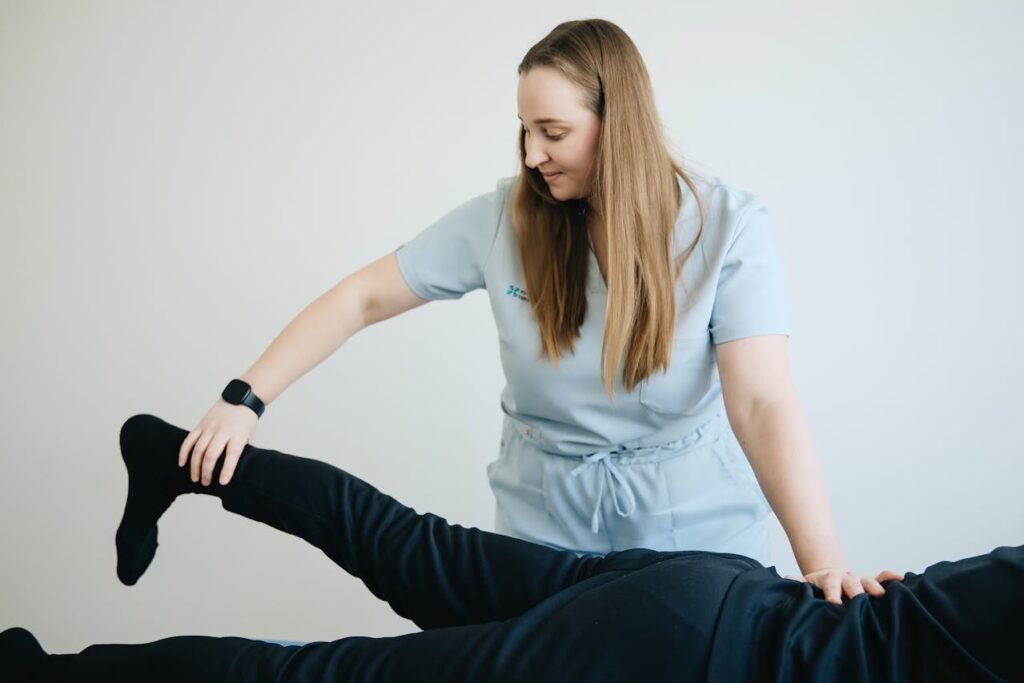

Both physiotherapy and physical therapy aim to help people move better, feel stronger, and live with less pain. A treatment plan emphasizes personalized care, including guided exercises and patient education, focusing on physical therapy and physiotherapy.
Therapeutic modalities include:
-
Heat therapy, which improve blood circulation and flexibility, including deep heat
-
Cold therapy, which reduces inflammation and pain
-
Strengthen muscles through strength-building exercises, essential for improving conditioning using resistance methods.
Integrating methods from both therapies can lead to significant improvements in pain levels and functional status for patients. Aquatic therapy allows for low-impact exercises in water, relieving stress on joints while enhancing mobility.
Choosing Between a Physiotherapist and a Physical Therapist
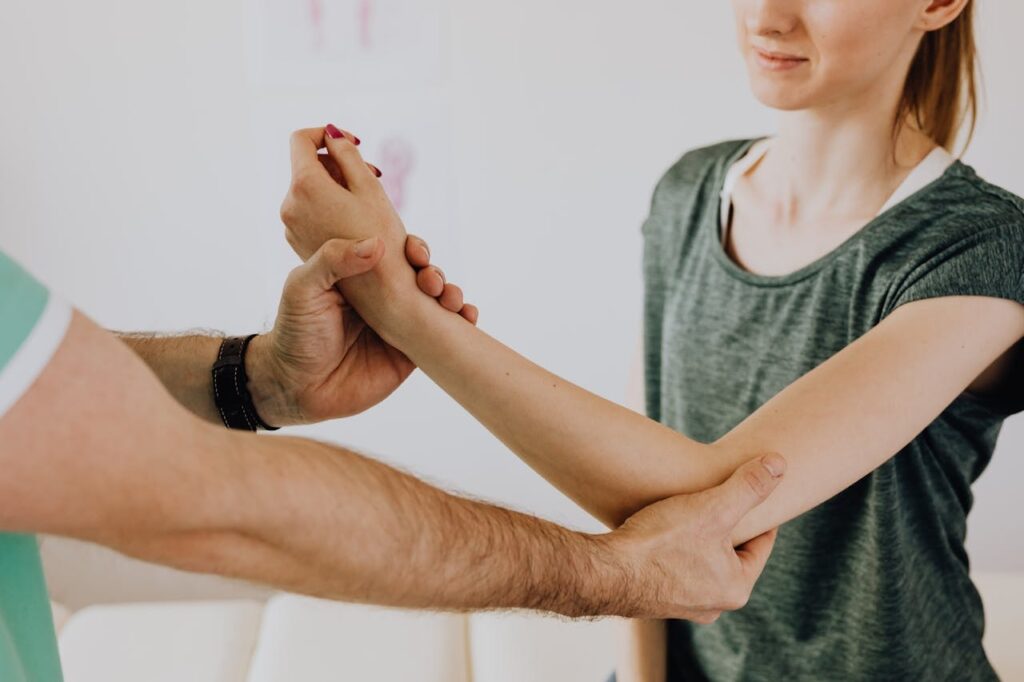

Choosing between a physiotherapist and a physical therapist depends on the credentials, experience, and approach of the provider. Patients should research and find a specialist that aligns with their specific health needs.
Physiotherapists help with recovery in hospitals, clinics, or rehabilitation facilities, while physical therapists primarily focus on exercise-based treatments. Consulting your primary care doctor can also provide options for finding a physiotherapist.
Integrating Physiotherapy and Physical Therapy for Optimal Results
Combining physiotherapy and physical therapy provides patients with personalized access to care programs, promoting better engagement in their recovery process. This integrated approach offers a comprehensive care strategy to address various physical ailments and enhance recovery.
Conditions such as sports injuries, chronic pain, and post-surgery recovery greatly benefit from the holistic treatment strategies offered by integrating both therapies to treat chronic conditions. This approach leads to improved outcomes and higher patient satisfaction levels.
Summary
To sum up, physiotherapy and physical therapy share many similarities but also have distinct differences in their approach and techniques. Both aim to help patients move better, feel stronger, and live pain-free lives by focusing on personalized care and therapeutic interventions.
By integrating both therapies, patients can benefit from a holistic approach to treatment, leading to improved outcomes and overall satisfaction. Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain, recovering from surgery, or looking to enhance your physical function, understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are physiotherapy and physical therapy the same?
Physiotherapy and physical therapy are functionally identical, with the terms used interchangeably depending on the region. Thus, there is no significant difference between the two.
What are the main focus areas of physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy primarily emphasizes a holistic approach, promoting physical activity while offering hands-on treatments. This ensures comprehensive care for various physical conditions and recovery needs.
What techniques do physical therapists use?
Physical therapists commonly employ exercise routines, hot and cold therapies, ultrasound, and TENS, along with advanced methods such as cryotherapy to aid in rehabilitation. These techniques are integral to promoting recovery and restoring function.
What qualifications are required to become a physical therapist in the U.S.?
To become a physical therapist in the U.S., you need a Bachelor’s degree, a Doctoral program in physical therapy, and must pass a state licensure exam. These qualifications are essential to practice professionally in the field.
How can combining physiotherapy and physical therapy benefit patients?
Combining physiotherapy and physical therapy offers patients a comprehensive care approach that addresses multiple physical ailments, leading to improved recovery outcomes. This integrated method ensures a thorough focus on each patient’s needs, optimizing their rehabilitation process.
Dr. Adam Babcock PT, DPT
“We Help Active Adults Quickly Recover From Pain Or Injury So They Can Stay Active, Get Back To What They Love To Do, and Do It For Decades”






